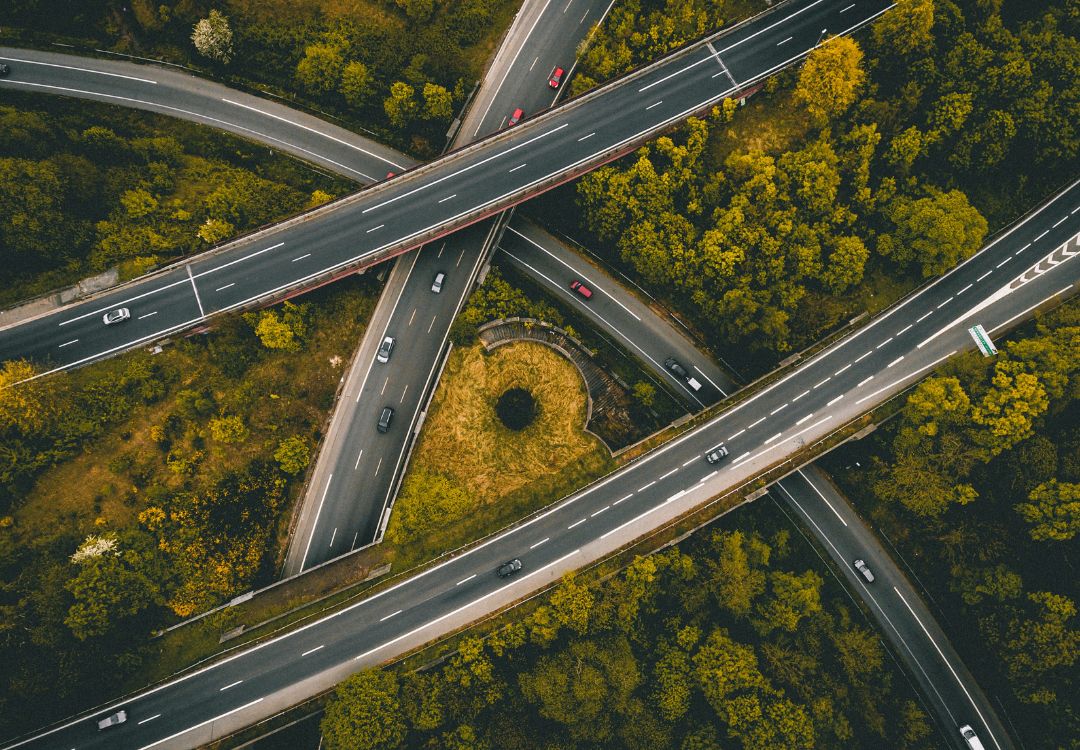
ClearWay™ is our automatic incident detection (AID) system which utilises our long-range, high-resolution radar sensors, combined with rules-based software, to detect and track all activity on a highway. Its role is to analyse the behaviour of the traffic and identify critical incidents such as stopped vehicles, wrong-way driving and pedestrians moving on the highway. In addition, the same system can provide further actionable data such as vehicle count and classification, and traffic flow information.
The radar sensors deployed as part of ClearWay™ require a clear line of sight for optimal performance, just like other roadside sensors such as CCTV.
If the growth of trees and bushes at the side of the highway, especially during the summer months, remains unchecked, could it impact the coverage of line-of-sight sensors?

Navtech Radar’s research and development team needed to explore new and existing techniques to find a solution that might work. After considering several options, we selected a promising method which was originally developed to compare the performance of a radar against a known baseline.
One of the key advantages of our Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar is that they see everything in their environment, not just moving objects. A full rotation of radar data includes all elements within the detection range such as buildings, fences, trees, and hedges. This allows us to take a baseline image of the environment for a given point in time, which can then be compared against all future snapshots to look for significant change. Our designed method of comparison analysed every power reading within the high-resolution radar data using the mean squared error, which could then be aggregated to evaluate how each part of the image had changed; an approach which worked very well.
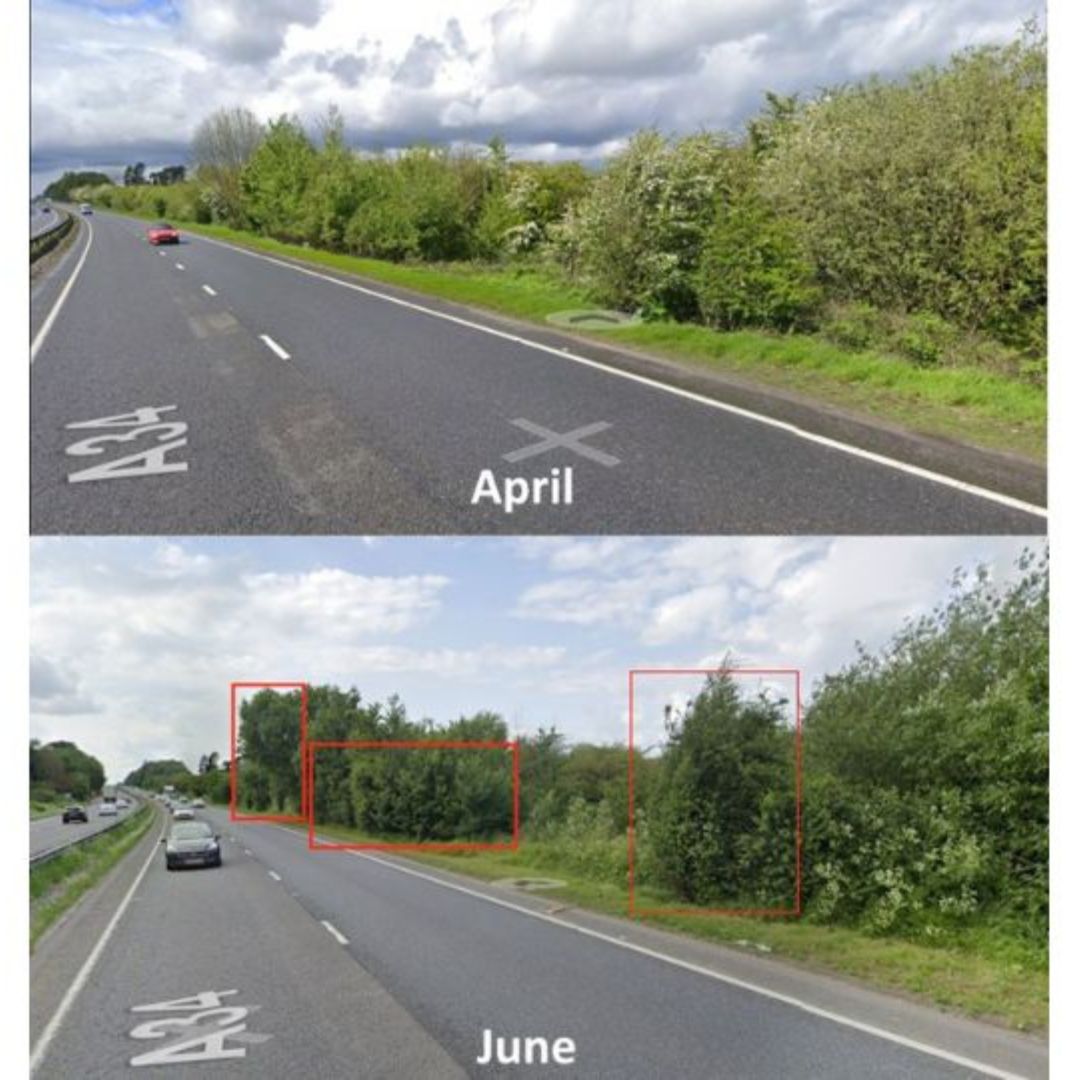
Figure 1: Google Street View
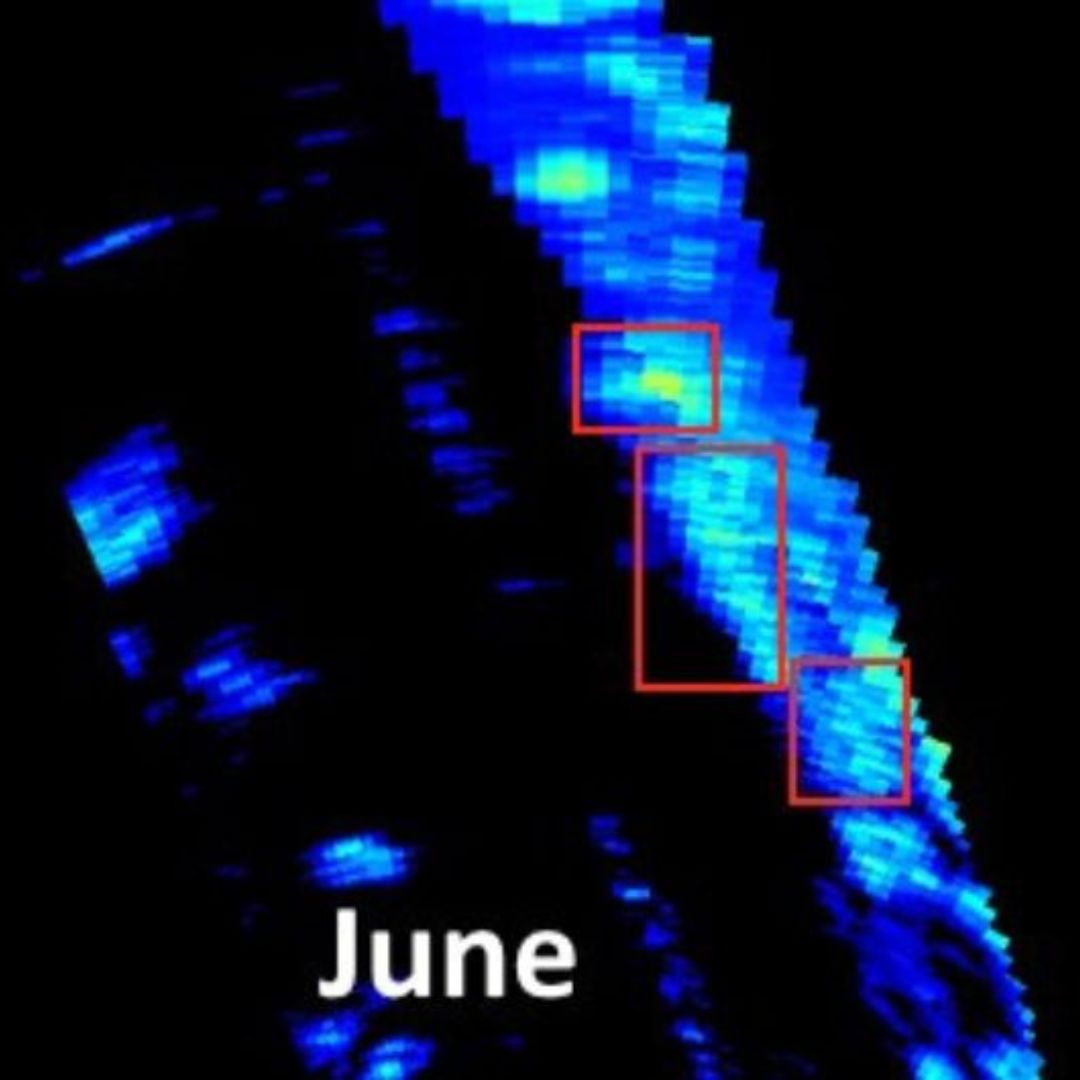

Figure 2: Radar View
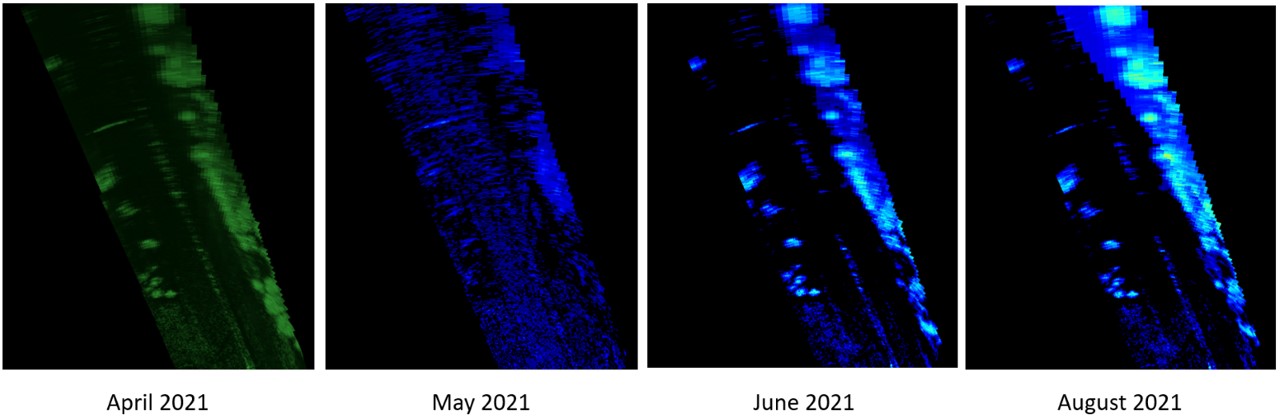

This innovation opens up other possibilities for monitoring the environment using the radar.
Due to the high resolution of our sensors, their reliability and capability to analyse their surroundings in all-weather conditions, they are extremely well-suited for detecting environmental changes, both large and small. The data our system provides can be used to remotely determine the need to take remedial action to preserve line of sight coverage by a range of sensor technologies.